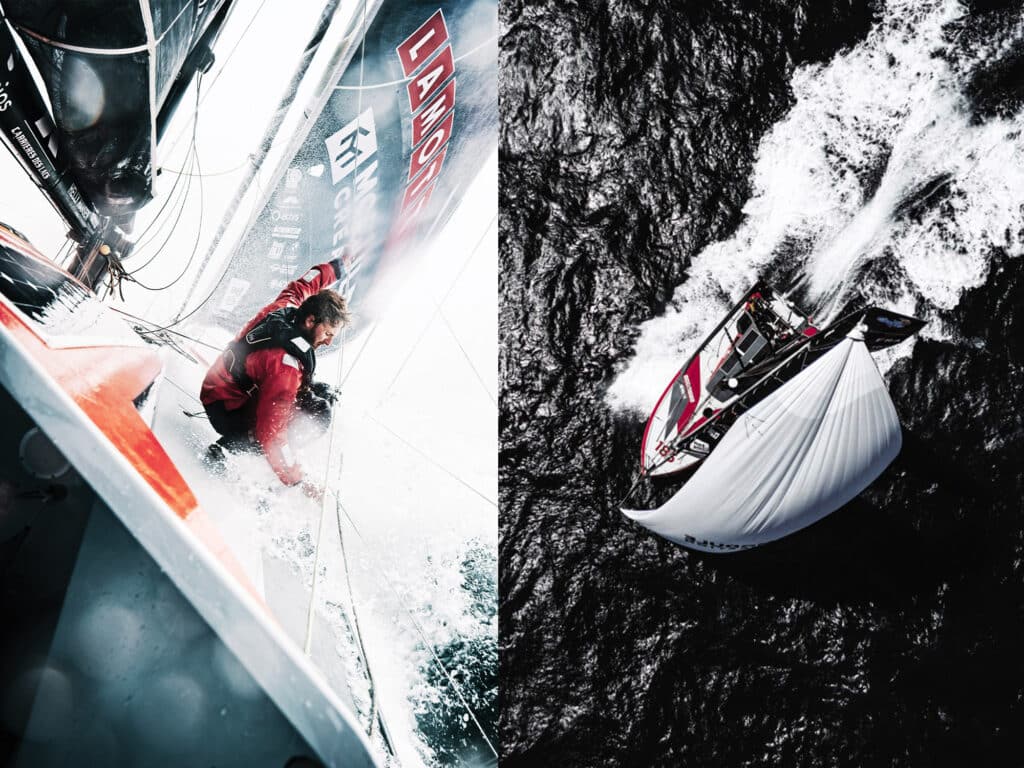
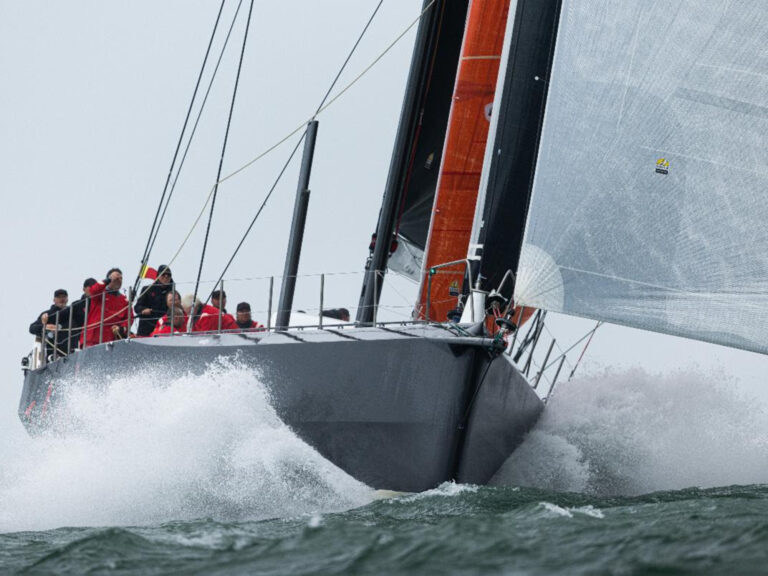
For sailing fans visiting from outside France, the Route du Rhum is a cultural shock, barely to be believed even once seen. It is France’s oldest singlehanded race, first held in 1978, and run every four years from St. Malo in northern France 3,500 miles across the North Atlantic to Guadeloupe. The fleet of 138 boats that assembled for the start in November 2022 was incredible, with an estimated value of 260 million euros—from the implausible 100-foot Ultime trimarans to a record fleet of 38 IMOCA 60s and a similarly impressive fleet of 55 Class40s. Dock sides are crammed with spectators, many hoping to catch a glimpse of the top skippers—some are genuine sports stars. Had the 2022 start not been delayed, French President Emmanuel Macron was to have attended. It’s that much of a big deal.
In the days and hours before the Route du Rhum started, more than 1 million people passed through its race village in St. Malo. In this environment, even non-French amateurs, such as the two US Class40 skippers, Alex Mehran and Greg Leonard, gained celebrity status with relentless autograph signing, selfies with fans and press interviews. Usually outshone by the bigger, higher-profile boats, the Class40 is the most successful 40-footer of all time. While the Farr 40 never topped more than 40 boats at a world championship, this is the second Route du Rhum in which more than 50 participated. To date, 192 Class40 hull numbers have been allocated.
While “Open 40s” once competed in the OSTAR and Around Alone, the Class40 came about independently. Born in France in the early 2000s, two designs defined the class: the Pogo 40 and the Jumbo 40. But the success and longevity of the Class40 is due to its highly constrictive box rule, drafted by a group that includes wise French sailor and journalist Patrice Carpentier, which remains robust 18 years on.
The box rule’s basic parameters are a maximum length overall of 39 feet, 11 inches; max beam of 14 feet, 9 inches; draft of 9 feet, 10 inches; average freeboard of 3 feet, 6 inches; max mast height of 62 feet, 4 inches; max working sail area of 1,238 square feet; minimum displacement at 10,097 pounds; and max water ballast of 1,653 pounds per side. Most brutal are the materials limitations: Carbon fiber, aramid, honeycomb cores and pre-preg resin are forbidden from the construction of the hull, deck, interior structure and fittings; go down below on one and, joyously, thanks to the GRP construction, it is not coffin black.
Carbon fiber is permitted for the mast, boom and bowsprit, while standing rigging must be steel rod. Sails are limited to eight, and all but two and the heavy-weather jib must be polyester and nylon. A single fixed keel and as many as two rudders are permitted, but daggerboards and foils are banned, as are canting, rotating masts, mast jacks, and adjustable or removable forestays. However, complex kick-up rudders are permitted. (Although their effectiveness to kick up in a collision is allegedly dubious.) Over the years, displacement and average freeboard have slightly reduced, but the biggest rule amendment has limited “how scow” Class40 hull shapes can be. While the latest foiling Protos in the Classe Mini (the “flying bathtubs”) are fully flat-bowed, Class40 has two max beam limits just short of the bow to prevent this. Naturally, costs have risen, but the rule has successfully limited them; today, a top Class40 costs 700,000 to 800,000 euros.
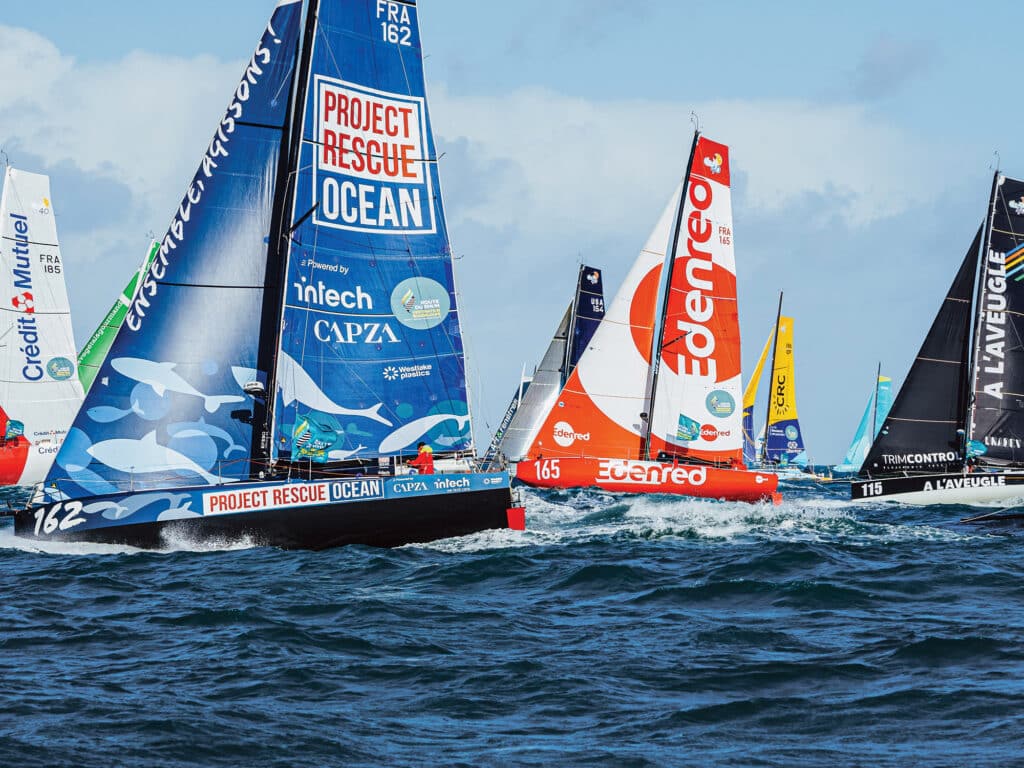

Those sailing the Class40s in the early days were a mix of pros and amateurs. Today professionals on sponsored boats are the majority. As for aspirant French pro sailors, the Class40 has become a significant stepping stone between from the Classe Mini and Figaro circuits to the IMOCA.
As skipper of Groupe SNEF, leading Mini and Figaro skipper Xavier Macaire says: “The transatlantic races like this [Route du Rhum] are very interesting to us, and the boat is not very expensive. The Class40 is easy to maintain and prepare, and is not a complicated boat like an IMOCA where you need 12 guys. With this, you need two or three, not full time. It is an easy, fast boat.”
With more top pros like Macaire joining, 30 new Class40s have been launched in the last four-year cycle. The most recent Route du Rhum podium, for example, comprised two-time Solitaire du Figaro winner Yoann Richomme (Paprec Arkea) and Mini Transat winners Corentin Douguet (Queguiner-Innoveo) and Ambrogio Beccaria (Allagrande Pirelli) of Italy.
Of the French classes, the Class40 and the Mini remain the most cosmopolitan, with entries from other European countries, notably Italy at present, while the United States, Australia and South Africa were also represented in the Route du Rhum. Far from being put off by the pro element, Americans Alex Mehran and Greg Leonard were thrilled to be on the same starting line. “It is such a privilege to race against some of the top offshore sailors in the world,” says Leonard, who hails from Florida. “It is like playing football against a first team in the NFL—it is that level of quality. There are not that many sports you can do that in.”
Both American skippers came to the Route du Rhum from similar paths. With his Mach 40.3 Kite, Leonard is a professional economist originally from Texas. He campaigned a J/120 for many years with his remarkable son Hannes, who raced his first doublehanded overnighter with his father at age 13. Now 18 and with thousands of race miles under his belt, both in the US and Europe, he is a Class40 expert. For his father, the Route du Rhum was his first singlehanded race.
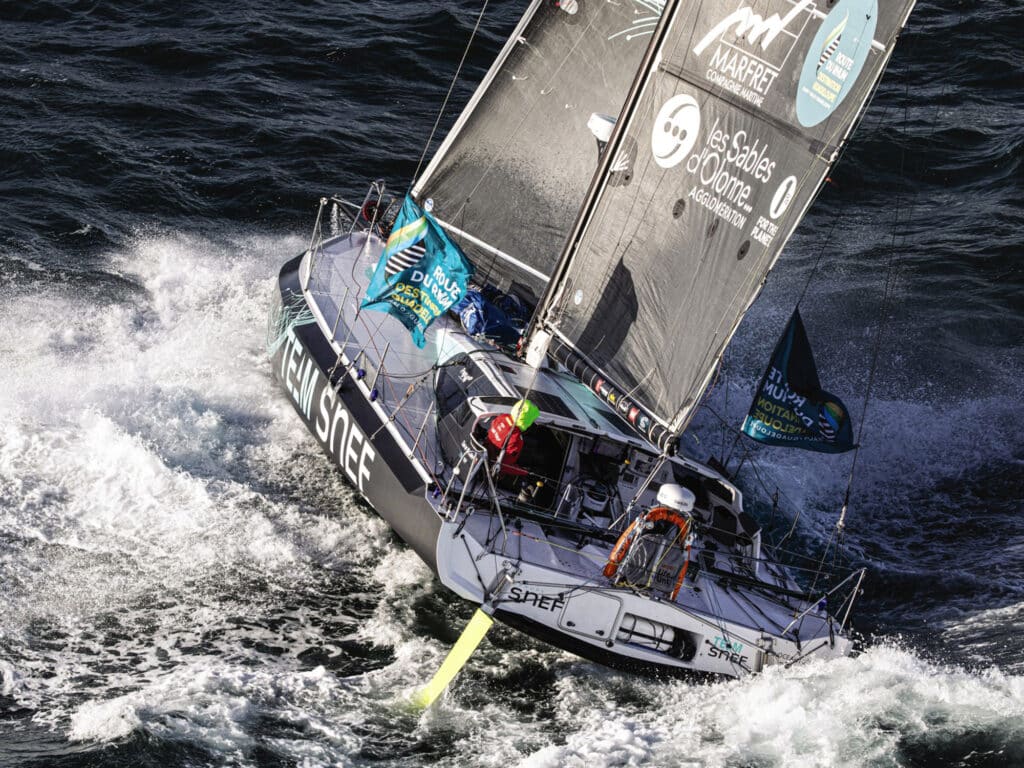

Over the years, several top shorthanded sailors, notably British Vendée Globe skippers Mike Golding and Miranda Merron, have raced with him, also coaching him. He is very enthusiastic about the Class40: “They are beautiful boats, such fun to sail. When we delivered her to St. Malo, we had 28 to 40 knots just aft of the beam, and we just hung in the low 20s boatspeed, and it was finger-light steering.”
Mehran skippers Polka Dot, which has the perfect pedigree, being Yoann Richomme’s 2018 Route du Rhum winner—a Lift V1 design. Growing up as part of the St. Francis YC Laser squad and subsequently a Brown collegiate sailor, he met Welsh Class40 designer Merfyn Owen in 2009 and raced one of his designs. Remarkably, he won his first major singlehanded race, the 2009 Bermuda 1-2. He subsequently graduated to an Owen Clarke-designed Open 50, in which he set a record in 2012’s singlehanded Transpac. He then went off, had four kids, and developed his commercial real estate business before getting the itch once more last year. He competed doublehanded with Owen in the 2021 Transat Jacques Vabre on an old Class40, but as Mehran puts it, “We needed to get something scow.”
He too has been receiving coaching from Merron and Golding, among others. According to Mehran, one of the most difficult things to explain to those back home is less the offshore-racing fever that afflicts French fans, but that their skippers are not multimillionaires. Instead, they come from a wide age group and all have commercial backing to either buy a secondhand boat or—if they are higher-profile, more accomplished or just plain lucky—build a new one. So, returning to the Route du Rhum podium, Paprec’s business is waste disposal (admittedly, its owner races his own Wally 107), Arkea is banking and insurance, Queguiner is building materials, Innoveo is an app-development platform, and Pirelli makes tires (its CEO has a Wally 145).
Over the last two decades, the Class40s themselves have evolved, despite Draconian design limitations. What started as cruiser-racers with fitted-out interiors became racer-cruisers and are now refined pure racers. They may not be black inside, but the build quality of the latest-generation designs is of the highest standard, and it seems no longer possible to buy a cruiser-racer.
A delight of the Class40 is that no one designer is dominant; eight different designs make up the 30 boats built over the last four years. Pogo Structures, last of the original builders, is on its fourth version of its Pogo 40, the S4, designed by Emirates Team New Zealand’s naval architect, Guillaume Verdier (who also designed Structures’ scow-bowed flying Proto Mini).
The man who developed the first blunt-fronted scow Mini, David Raison, produced the Max40, built by JPS in La Trinité-sur-Mer. Also built by JPS are Sam Manuard designs—the Mach 40.4, such as the 2021 Transat Jacques Vabre winner Redman, skippered by Antoine Carpentier (nephew of the original rule’s writer), and now its evolution, the Mach 40.5, of which two competed in the Route du Rhum.
In 2020, VPLP made its first foray into the class with the Clak 40, built by Multiplast, of which four raced in the Route du Rhum, the top finisher being Martin le Pape’s Fondation Stargardt. Etienne Bertrand, another successful Mini designer, had two Cape Racing Scow 40s in the race, while Allagrande Pirelli, believed to be the most expensive of the latest crop and campaigned by last year’s Mini Transat winner, Ambrogio Beccaria, is an all-Italian affair designed by Gianluca Guelfi and built by Sangiorgio Marine Shipyard in Genoa.
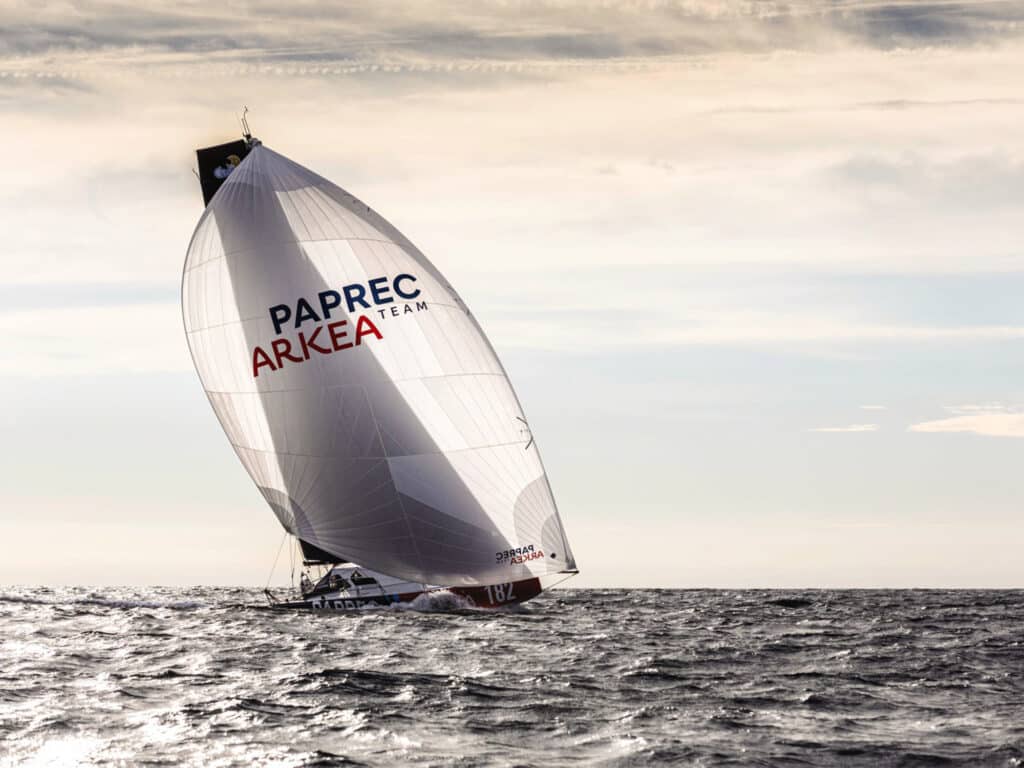

However, after the recent Route du Rhum, nosing in front in the design race is Marc Lombard with his Lift V2s, of which seven were racing, including Yoann Richomme’s winner, Paprec Arkea. Lombard is one of the longest continuous players in the Class40, and has worked with Tunisian manufacturer Akilaria on its RC1, RC2 and RC3 models since 2006, of which 38 were built. His latest designs have been the Lift, introduced in 2016; Veedol-AIC, one example, took Richomme to his first Route du Rhum victory. The Lifts were custom-built with a hull and deck made by Gepeto in Lorient, but finished off by the V1D2 yard in Caen, and were more precisely engineered and built than the Akilarias. They were superseded this cycle by the Lift V2, the most popular of the new Class40s, with seven competing.
For Richomme, the Route du Rhum was a small distraction from having a new IMOCA built. He entered the Route du Rhum to defend his title and stay race-fit. If the first Lift was an early scow, the present one is at the limit, to the extent that it has a bump in the hull 2 meters aft from the bow at the limit of where the Class40 rule restricts the max beam to prevent such extreme scowness.
The scow bow provides more righting moment, but it also does interesting things to the boat’s hydrodynamics. “With a pointy bow, the keel is more angled and creates more drag,” explains Richomme, who is also a trained naval architect. “When a scow heels, the hull is almost parallel to the keel, so sometimes when we go over the waves, we can feel the keel shudder when it is producing lift. The chine is low and therefore very powerful, and when we heel, it makes for a very long waterline length. Also, we have very little rocker, whereas other [new] boats have a lot, which creates a lot of drag so they don’t accelerate so well when they heel.”
The Lift V2 “is a weapon reaching,” Richomme says. “We can hold the gennaker higher than we used to. Last time, I didn’t even take one. But with the power going up, so have the loads, and we are having problems with the hardware. I have broken two winches already.”
A downside of the big bow and straight chine is downwind, where the technique seems to be preventing the bow from immersing. Paprec Arkea is typically trimmed far aft, including the stack and the positioning of the 1,653 pounds of water ballast (most new boats have three tanks each side), while its engine is 19 inches farther aft, and the mast and keel 11 inches farther aft than they were on his previous boat. They are 77 pounds below the minimum weight, which Richomme admits may be too extreme—during training they broke a bulkhead.
Otherwise, their increased cockpit protection is most noticeable on all the new designs (although not to IMOCA degrees), while most have a central pit area with halyards fed aft from the mast down a tunnel running through the cabin. On Paprec Arkea, a pit winch is mounted just off the cockpit sole. With the main sheet and traveler lead there as well, Richomme can trim from inside the cabin.
Most extraordinary about the scows is how fast they are. Anglo-Frenchman Luke Berry, skipper of Lamotte-Module Création, graduated from a Manuard Mach 40.3 to a 40.5 this year and says: “It is a massive improvement both in speed and comfort. Reaching and downwind, we are 2 knots faster, which is extraordinary.”
The top speeds he has seen are 27 to 28 knots. “Most incredible are the average speeds—higher than 20.”
This effectively turns yacht-design theory on its head, with waterline length and hull speed having less effect upon defining the speed of a boat that spends so much time planing. On the Mach 40.5, the waterline is just 32 feet, with a length overall of 39 feet. Compared to the Lift V2, it has more rocker, supposedly making it better able to deal with waves.
Nowhere is the speed of the latest Class40s more apparent than where they finished in the Route du Rhum in comparison to the IMOCA fleet. Paprec Arkea arrived in Guadeloupe ahead of 13 IMOCAs, or one-third of the way up the IMOCA fleet. Richomme says he used to sail on a Lombard-designed IMOCA 20 years ago, when they would make 10.5 knots upwind. “On a reach, I reckon we are faster than them now. We can do 20 to 22 knots average speed.”
Ugly seems to be quick, but when it comes to the Class40, beauty is in the eye of the beholder of the trophy.