When approaching the leeward gate, there are a lot of possibilities to consider: Which mark to round? How to best round it? What’s the exit and the next windward leg plan? All of this needs to be discussed on the run so your overall game plan is clear well in advance. It’s much easier with a single leeward mark, in which case you can jump ahead to the next section—the approach—and focus on techniques used for rounding the left-hand gate, which is likely what you’re doing when there is only one leeward mark. But when there are gate marks, things get complicated, and the tactician has a number of factors to consider. Let’s start by defining your choices.
Closest and most windward mark: If the gate marks are in place before the start, it is usually possible to sight them with a hand-bearing compass and then determine the wind direction that would make them square (add or subtract 90 degrees depending on which way you sighted). The mark that is farther upwind should be closer, similar to the favored end of the starting line.
Most favored from where you are: The mark that is farthest upwind (or highest ladder rung) might not be the most favored from where you are in the moment. In other words, if you approach from one side of the course or the other, the mark which you can round soonest is probably favored for you.
Least crowded: This is important, especially if you’re stuck in a pack of boats.
Cleanest air: With the approach and the exit looking upwind, consider where the fewest obstructions and the best wind will be. One good test of the favored-gate mark is when two boats round opposite marks simultaneously and continue on opposite tacks. After the fleet is cleared, if both boats tack, the boat that is ahead probably had cleaner air and perhaps rounded the favored or closest mark.
Most advantageous current: Rounding the down-current mark will usually make an easier and faster turn. However, there may be tactical or strategic advantages to the up-current mark. When the current is running across the course—i.e., from one gate mark toward the other—it’s usually best to round the down-current gate (the mark toward which the current is running) because the rounding will be easier and the boat will get there faster due to the movement of the current.
The Final Approach
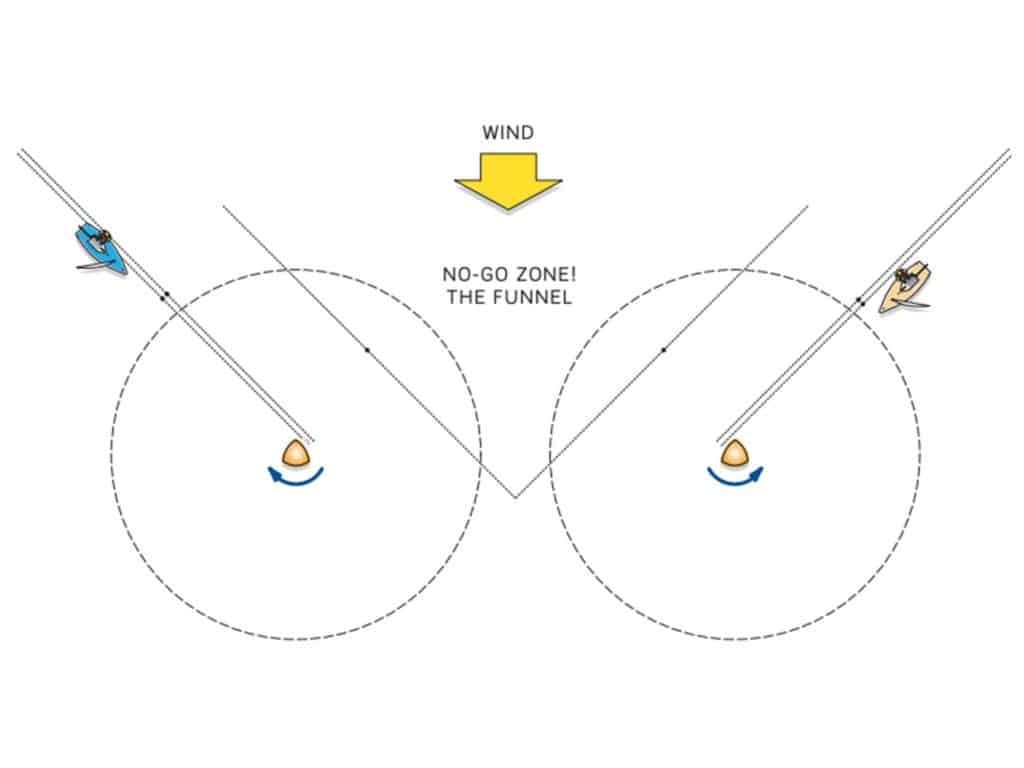
The goal here is to work hard to be the inside or farthest ahead boat. One way to do so is to stay out of the “no-go zone” in the middle. Approach one of the gate marks from outside the funnel and maintain boatspeed while avoiding bad air.
We learned about the no-go zone the hard way at an Etchells Worlds. We were caught back in the pack (50ish in a 90-boat fleet) and stuck smack in the middle of the funnel, with boats pouring in from both sides. The race committee had set the marks so close that there were less than six boatlengths between them, which meant the three-boatlength zones for each mark overlapped. We intended to round the left mark, but boats to the left of us were telling us to turn right for the right-gate mark while boats to the right of us, who also wanted the left mark, were telling us to turn left for the left mark. Eventually, the funnel overfilled and the whole group converged, locked rail to rail with no one able to turn. The lesson here is to prioritize being inside—with rights, of course.
Approach the three-boatlength zone with the most speed possible to obtain or break later overlaps. It’s imperative to be vocal if you have rights, or if another boat does not have rights and is trying to take inside room. The observation moment for whether an inside boat obtains an overlap and therefore has rights to room inside is when the leading boat of your group that is overlapped and rounding together reaches the three-boatlength zone. If you have been overlapped or not overlapped with another boat for a minute or more as you approach the leeward gate marks, and it suddenly changes, be sure to let the other boat know you have either broken the overlap or established it as soon as that occurs. And remember, Rule 18.2(e) (Giving Mark-Room) says: “If there is reasonable doubt that a boat obtained or broke an overlap in time, it shall be presumed that she did not” (obtain or break the overlap before the first of the two boats reached the zone).
If a boat tries to establish a late overlap to windward of you, your best defense is to luff them above the three-boat-length zone, and then bear off sharply to break the overlap and get your bow into the zone. This defense works well on both port jibe to the left gate and starboard jibe to the right gate.
A common mistake is getting pinned beyond the laylines when both boats are outside the zone. Rule 18 (Mark-Room) does not apply until one of the boats is in the zone, so it’s important to understand the nuances of the rules in this situation.
And here’s a quick tip on spinnaker handling when approaching the zone: Count down the drop for the crew to hear. Usually, the tactician will provide a 30-second warning and then a 10-second countdown. Once the count is established, the pit, crew boss or bow person should also voice the countdown. For boats with string takedown systems, the sheet is released (slacked) sometimes as late as 2 on the countdown.
The Strategic Rounding
Once we’ve decided which gate mark we want and where we want to go on the second beat, we have to manage and optimize the rounding strategically. Let’s first tackle the standard reaching approach, which is by far the most common and generally regarded as the easiest method.
Some types of boats may require a brief bear away to unload pressure on the spinnaker and facilitate its drop. So, we need to reach into the mark a little high of the layline, allowing the time we need to finish the bear away, and then head up to a fast reaching course.
Another approach is to jibe around the left-gate mark (aka the “Mexican”). Here, we come in, usually at a hot angle, on starboard with rights until reaching the protection of the three-boatlength zone, where the mark-room rule begins to apply. The spinnaker is usually coming down on the left side of the boat, and a wide jibe rounding makes the douse easy for the crew. The douse is ideally left so late that the boat is already jibed and on port jibe, so the spinnaker falls on the new windward (port) deck.
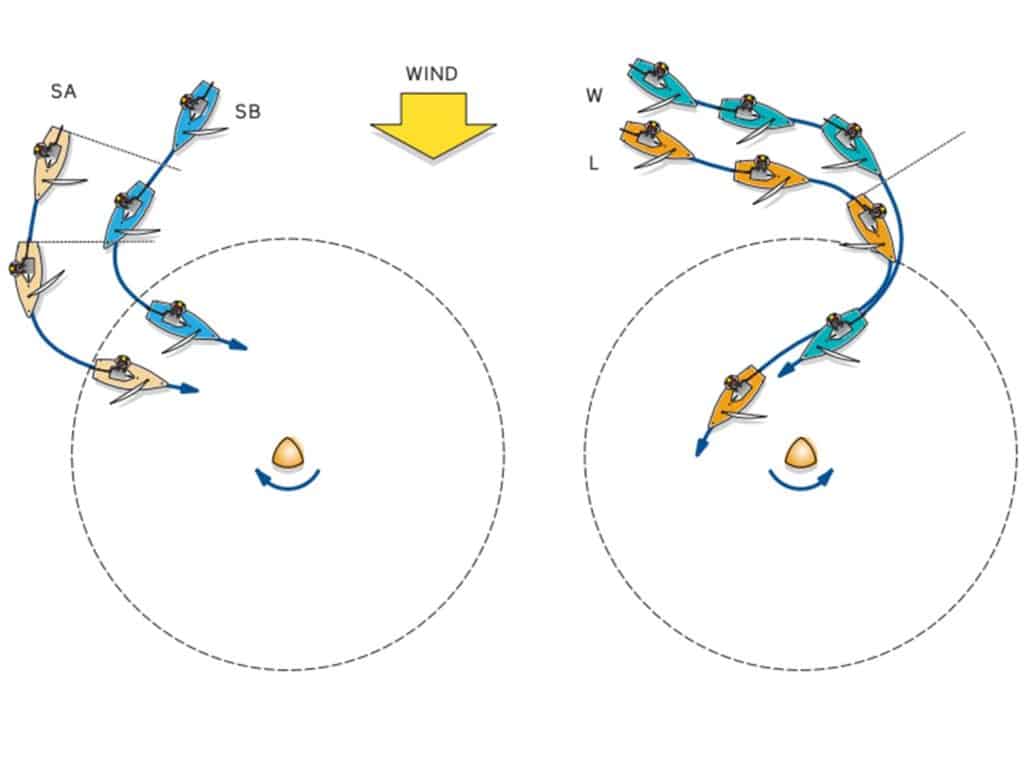
Left diagram: At Position 1, SA is clear ahead of SB, so SA is the right-of-way boat under Rule 12 (Clear Ahead/Clear Astern). But SA cannot jibe onto port without fouling SB, who would still be on starboard under Rule 10 (Port/Starboard). Because SB is clear astern, no rule requires it to jibe and sail to the mark. SB is pinning SA and can sail it well past the layline. The tactic for SA is to bear away (or slow down) and cause the boats to become overlapped (Position 2). Because SB has become overlapped from clear astern, Rule 17 (Proper Course) requires it to sail no higher than its proper course, which means it has to jibe to sail to the mark. If SA jibes when SB jibes, it will be overlapped on the inside and entitled to mark-room under Rule 18.2(b) (Mark-Room).
Right diagram: W has overtaken L to windward from astern, so Rule 17 does not apply. L can sail as high as it wants and keep W from reaching the zone. Then L can bear away and enter the zone clear ahead of W (see Position 3) and sail where it wants in order to make a “tactical rounding.” Kim Downing
We perfected Mexican drops on the TP52 Spookie using a string takedown system. The crew trained me to pause the turn, nearly dead downwind, as soon as the boom jibed. At that moment, the chute was dropped onto the port (and now windward) deck. It was counterintuitive at first, but it worked so well, I readily adopted the technique. We proceeded to mimic the maneuver with a new name for the right-gate mark called the “Rodeo” drop. That way, the crew always knew exactly what type of drop and rounding to expect. The Rodeo goes like this: We’re on port jibe and want to go around the right-gate mark. We stay wide outside the funnel to ensure an inside overlap at the zone and jibe onto starboard around the mark. The spinnaker is still coming down on the left side of the boat. The Rodeo differs from the Mexican in that the spinnaker will end up to leeward.
A third approach—the “Flop”—is a specialty maneuver for certain asymmetric-rigged boats that is used when you can’t quite lay the mark without jibing, but don’t really want to complete a full jibe. A similar technique can be used on symmetric spinnaker boats, possibly by removing the pole and trimming the sheet and guy outboard by hand or foot. The Flop should only be attempted in moderate winds, flat water and clean air. It does not work in light or heavy winds. In light air, there simply is not enough wind pressure to keep the spinnaker full; in heavy air, it can become unstable and hard to handle, and lead to a spectacular wipeout.
When flopping, the boat goes wing-on-wing, meaning the main and asymmetric sails are flying on opposite sides. Ease the tack line by 15 percent of the boatlength as you bear away to by the lee to encourage the asymmetric to fill, and then return to slightly above a dead-downwind course. A successfully performed Flop is a very sharp arrow for your quiver and should be practiced to perfection. There are several variations of the Flop, and it is possible to jibe either the asymmetric or the mainsail. We have even tried a “Double Butterfly” by jibing both the main and asymmetric at the same time. I have never seen it attempted before—or since—and I wouldn’t recommend it again, but it did work.
Executing the Rounding
With approach determined, the next focus is the execution of the rounding. Here’s where we need to address the term “seamanlike.” When the inside boat does not have right of way, it is only allowed enough room to make a seamanlike rounding of the mark (see the definition of “room”), which is a smooth, curved rounding that maintains speed and stays within a boatlength or so from the mark.
The next term to remember is “tactical.” When the inside boat has the right of way, it can make a tactical rounding, which basically means “swing wide and cut close,” all the while keeping maximum speed.
One of our options during our rounding is to intentionally slow down once we reach the zone. A brief slowdown can pay big dividends if it improves your rounding, especially if you would have been forced to the outside of the boat ahead had you maintained your speed. You always want to round behind boats you are giving room to and round close to the mark. The slowdown can be achieved by taking the spinnaker down early, overtrimming the mainsail, or weaving with the helm (using your rudder as a sort of brake). When and how much to slow the boat is an art form practiced by team racers.
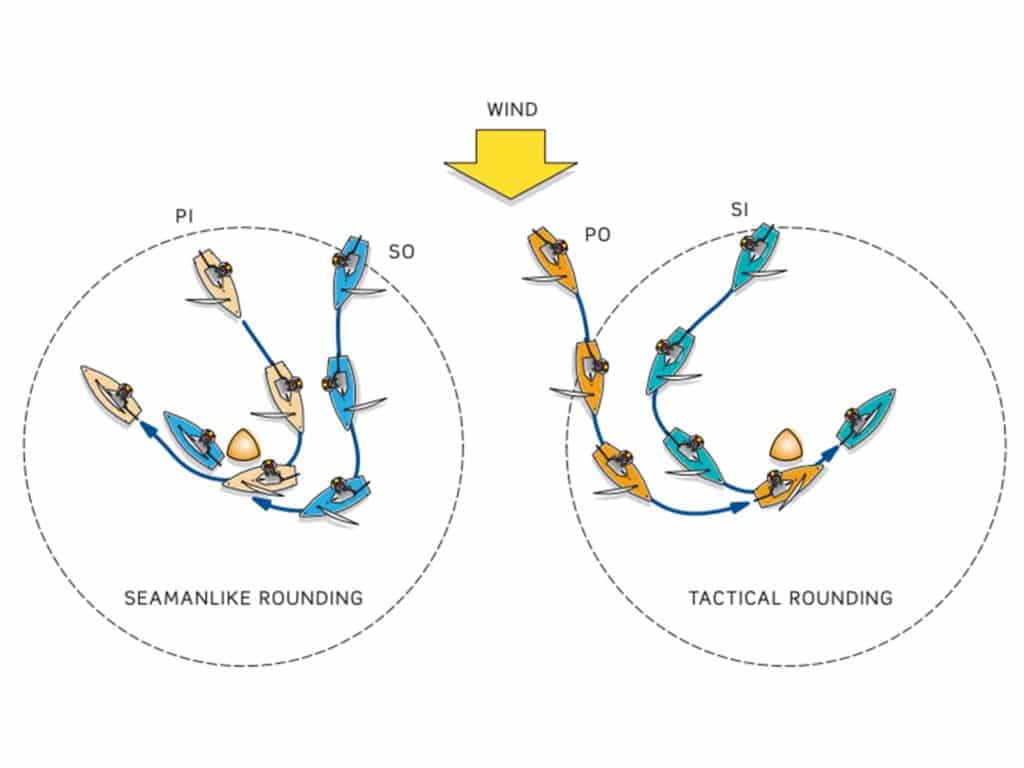
Left diagram: PI is on port tack, so it is the “keep-clear boat” under Rule 10 (Port/Starboard). However, because it is overlapped inside of SO, SO must give it “markroom” under Rule 18.2(b), which is just enough room to sail to and around the mark in a “seamanlike way” (typically staying within less than a boatlength from the mark throughout the turn).
Right diagram: SI is on starboard tack, so it is the “right-of-way boat” under Rule 10. While it is the right-of-way boat, it can go wider than mark-room. If this was a single leeward mark, Rule 18.4 (Jibing) would require it to sail no farther from the mark than its proper course. But Rule 18.4 does not apply at a gate mark (see the last sentence in Rule 18.4). Therefore, SI can sail as wide as it wants until it jibes, at which time it becomes a keep-clear boat under Rule 11 (Windward/Leeward) and must sail directly to and around the mark in a “seamanlike way.” Kim Downing
On rare occasions, we might plan to tack around a leeward gate mark. This is usually a bad idea because it sends us straight back into the funnel, with its attendant bad air and confused sea state. The main reason to tack around a leeward gate mark is to take advantage of a windshift, especially if you have just made a big gain and are unsure it will continue (and may perhaps oscillate back the other direction, thereby negating or reducing your gain).
In special circumstances, it’s better to round outside of an inside boat we are giving room to; this we call “Round the Outside” (or “Buffalo Girl”). This move helps ensure we can punch out, getting our bow forward of the inside windward boat. This approach works only if we have our bow well forward of the inside boat as we approach the mark and are confident we can maintain a safe leeward position. The technique is simple: Keep speed up by making a more gradual rounding than the inside boat, which might have to do a sharp head-up, causing it to slow. If the inside boat sails over and blankets you, it’s game over. It’s a high-risk move, and if it goes bad, it usually results in losing several more boats rather than the one you tried to get around.
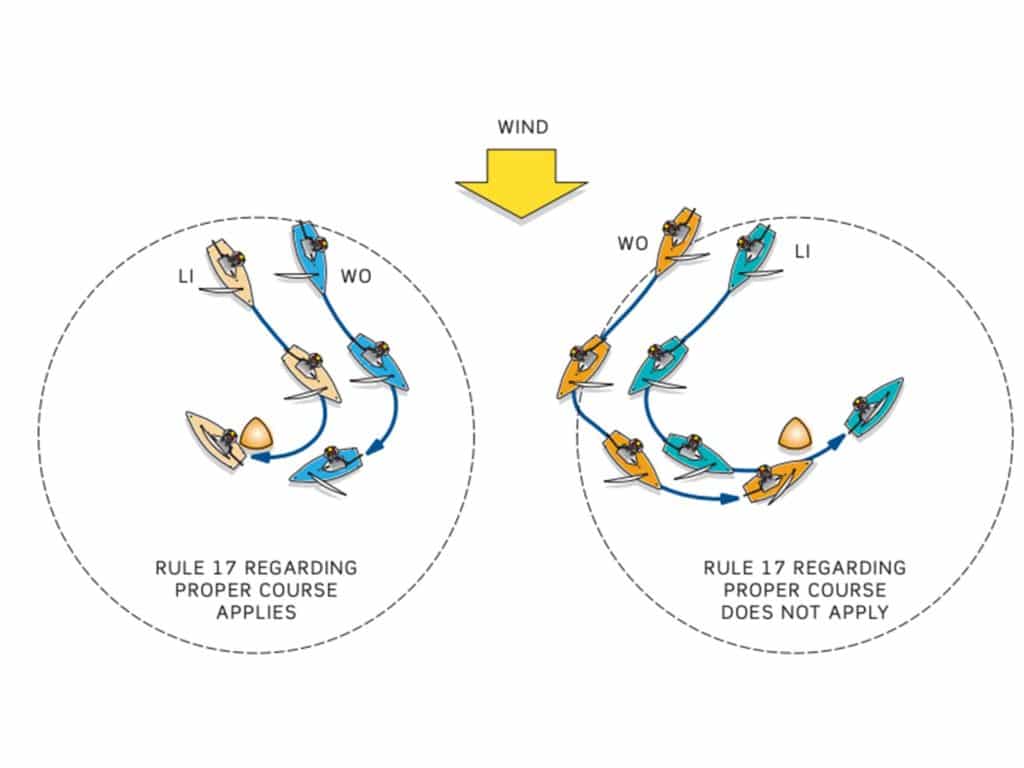
Left diagram: Before entering the zone, LI had established a leeward overlap on WO from clear astern within two of its lengths. Therefore, Rule 17 (On the Same Tack; Proper Course) applies and requires LI to not sail above its “proper course” while the boats are overlapped. Typically, LI’s proper course to round a mark will be approximately a boatlength or slightly more away from the mark, depending on the boat and the conditions.
Right diagram: In this scenario, WO had become overlapped to windward of LI from clear astern. Therefore, Rule 17 does not apply. Furthermore, because the mark is a gate mark, Rule 18.4 (Jibing) does not apply. Therefore, LI has no proper course limitation and can sail as wide as it wants to until it jibes, at which time it becomes a keep-clear boat under Rule 11 (Windward/Leeward), and it must sail directly to and around the mark in a “seamanlike way.” Kim Downing
The Exit Is Equally Important
The goals coming out of the gate include the following modes: fast, maximum VMG and boatspeed, with sails always correctly trimmed. As you round, the main must be trimmed ahead of the jib to add helm, thus reducing the amount of rudder angle needed for the turn.
Clear wind: Use your approach with reaching speed to coast slightly high of closehauled in order to hold a lane for as long as necessary while the tactician executes the exit plan. The tactician might want to hold high of the bad air from the boat(s) ahead by pinching in order to keep clear air to either maintain a lifted tack or continue toward the favored side of the course. Or the plan could be to tack as soon as the downwind traffic clears out. It’s rarely advantageous to foot through to leeward of the bad air from the boat(s) ahead.
Advantaged: If the gate you chose is favored (more upwind), then you should be able to tack and cross a boat that rounded the other gate. But just being ahead is not enough reason to tack. You need to continue on the lifted tack, heading toward the favored side of the course, and with clear air.
The ideal exit is all about flexibility, having the ability to tack when and if we want to, or just go as fast as possible and execute your strategy like you’d planned it on the run.
Rules at the Leeward Gate
Let’s now have Dave Perry, author of Understanding the Racing Rules of Sailing, take us through the roundings:
When two boats are overlapped as they enter the zone of a leeward gate mark, the inside boat will either be the “keep-clear boat” (windward or port-tack boat) or the “right-of-way boat” (leeward or starboard-tack boat).
An inside keep-clear boat is entitled to “mark-room” from the outside boat under Rule 18.2(b) (Giving Mark-Room), which is room to sail to and around the mark in a “seamanlike way” (see definition of “room”). If it stays within a seamanlike course, it is exonerated by Rule 43.1(b) (Exoneration) if it breaks Rule 10 (Port/Starboard) or Rule 11 (Windward/Leeward). Typically, that means the inside boat needs to stay closer than a boatlength away from the mark throughout its rounding. It is not entitled to room to make a “tactical” swing-wide or cut-close rounding.
On the other hand, an inside right-of-way boat can sail wherever it wants to, subject to a couple of limitations. Because it is a right-of-way boat, it does not need the protection of mark-room. Furthermore, Rule 18.4 (Jibing), which requires inside right-of-way boats to jibe around single leeward marks, does not apply at leeward gate marks (see the second sentence of Rule 18.4). Typically, inside right-of-way boats sail a tactical swing-wide or cut-close rounding. But with no Rule 18.4 at a gate mark, an inside right-of-way boat can sail farther from the mark than its proper course and delay or attack outside keep-clear boats during their roundings.
However, there are two limitations on how aggressive an inside right-of-way boat can be at a leeward gate mark:
1) If it became the leeward boat from clear astern, Rule 17 (On the Same Tack; Proper Course) applies and requires it to sail no higher than its proper course. Typically, but not always, when a boat enters the zone of a gate mark, it is fastest to round that mark. In that case, the leeward boat would need to jibe when its proper course was to jibe to round the mark.
2) Anytime a right-of-way boat changes course, it has to give the keep-clear boat room to keep clear under Rule 16.1 (Changing Course). If the right-of-way boat is changing course away from the mark, it is not sailing within the mark-room to which it is entitled, and so it is not exonerated by Rule 43.1(b) if it breaks Rule 16.1.